Russia-Eurasia
Eurasia is undergoing profound changes. While the Soviet past has left a lasting imprint, Russia and the countries of Eastern Europe, Central Asia and the South Caucasus have their own trajectory.
Related Subjects

How the US under Trump Became a Strategic and Ideological Adversary of Europe
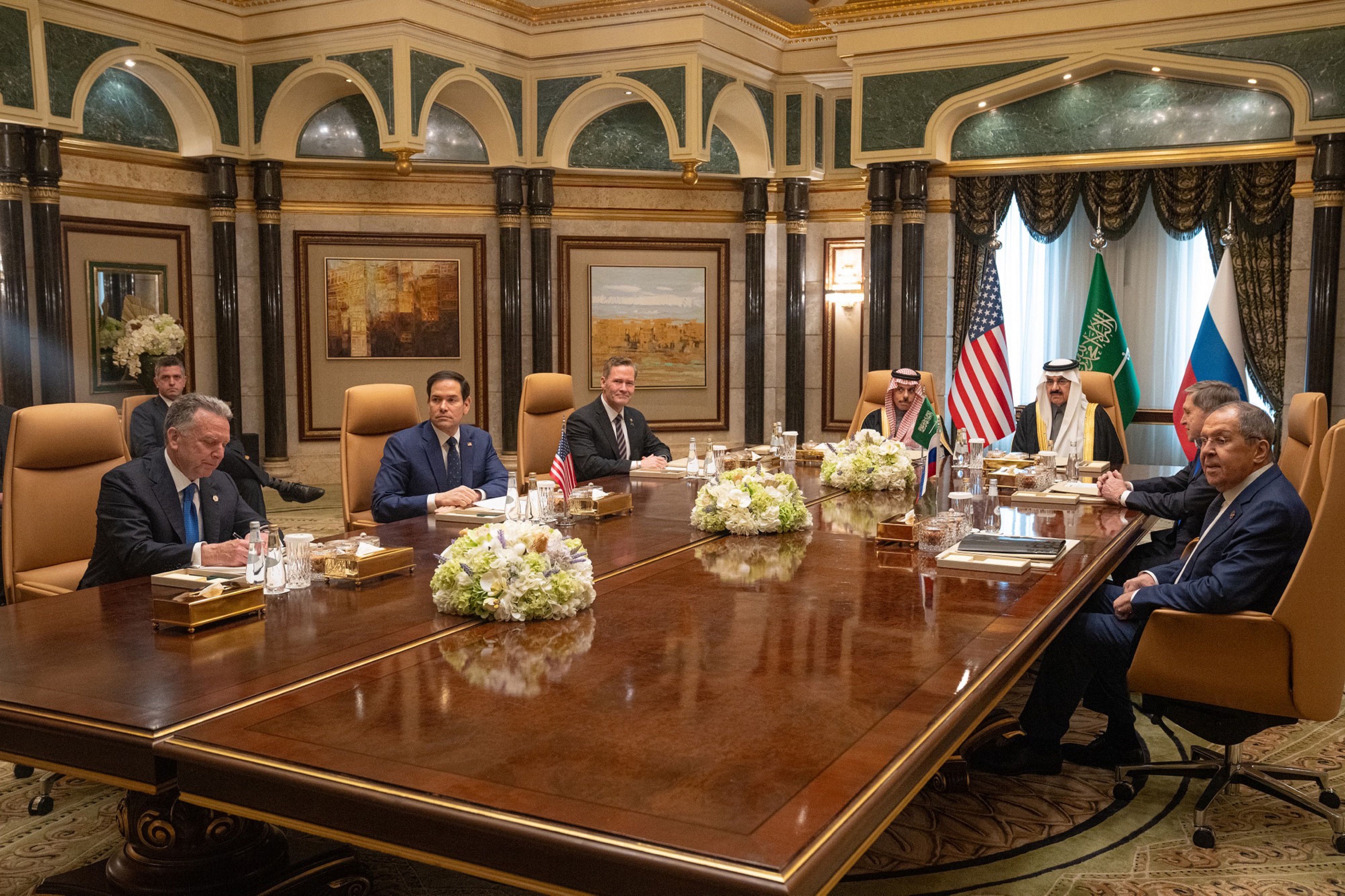

The Europeans' worst security nightmare seems to be coming true: on Tuesday, February 18, 2025, U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio and Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov met in Saudi Arabia to initiate the normalization of relations between their two countries. The meeting also aimed to set up peace negotiations for Ukraine. However, despite having the potential to affect the entire continent, the discussions took place without the Europeans or the Ukrainians being present.
Russian-Chinese Relations through the Lens of the SCO
Since 2001, the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) has played an important role in the improvement of Russian-Chinese relations. It has proven valuable for the expression of Moscow and Beijing's common interests at a regional level. However, the SCO is not insulated from potential difficulties in the Russian-Chinese relationship. Therefore, both countries hope that the organization can become a mechanism to manage tensions stemming from their sometimes divergent interests in Central Asia. However, to develop fully as an organization it must remain relevant to all its members, not just Russia and China.
U.S.-Russia Strategic Partnership against Nuclear Proliferation: From Declaration to Action
Higher Education in Russia. Potential and Challenges
In terms of higher education, Russia displays indicators worthy of enthusiasm.
Armenia, a Russian Outpost in the Caucasus?
Since the fall of the USSR, Armenia and Russia have sealed a strategic pact within the framework of the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO), the military arm of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). This political, military and economic alliance represents the strategic alliance in the South Caucasus, a region in the process of opening up. In the context of the 2008 Russian and Armenian presidential elections, it is interesting to analyze the relationship between these two states.


Support independent French research
Ifri, a foundation recognized as being of public utility, relies largely on private donors – companies and individuals – to guarantee its sustainability and intellectual independence. Through their funding, donors help maintain the Institute's position among the world's leading think tanks. By benefiting from an internationally recognized network and expertise, donors refine their understanding of geopolitical risk and its consequences on global politics and the economy. In 2024, Ifri will support more than 70 French and foreign companies and organizations.